P
Pascal (Pa)
A unit measuring pressure; airtightness tests
are commonly conducted with a pressure difference of 50 Pascals between inside
and outside.
Position of sun
The position of the sun in the sky, and hence the direction of the solar beam,
is described by the solar altitude and solar azimuth angles. The solar altitude
is the angle between the line to the centre of the sun and the horizontal plane.
When the sun is on the horizon, the solar altitude is 0°. When the sun is
directly overhead, it is 90°. The azimuth is the angle between true south
and the point on the horizon directly below the sun. By convention, it is negative
before noon and positive after noon.
The altitude and azimuth angles vary from hour to hour and season to season.
Positive pressure
A pressure above atmospheric.
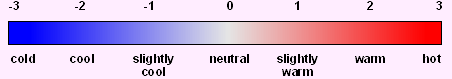
Predicted mean vote (PMV)
The predicted mean vote (PMV) is a thermal sensation scale. The mean opinion
of a large group of individuals expressing a vote on their thermal feeling under
different thermal circumstances has been used to provide an index to thermal
comfort. A PMV value of zero provides the optimal thermal comfort conditions.
A positive PMV value means that the temperature is higher than optimal and a
negative value means that it is lower. The comfort zone is generally regarded
as stretching from a slight feeling of cold (termed 'fresh', when the PMV is
-1) to a slight feeling of warmth (termed 'mild', when the PMV is+1).

Predicted percentage of dissatisfied (PPD)
The predicted percentage of dissatisfied (PPD) is an indication of the percentage
of people susceptible to feeling too warm or too cold in a given thermal environment.
It can be deduced from the PMV. If, for instance, the PMV
is in the range -1 to +1, then the PPD index shows that 25% of the population
will be dissatisfied. To reduce this figure to 10%, then the PMV has to be in
the range -0.5 to +0.5.
Primary energy (kWh or MJ)
The total amount of energy drawn from a primary source (oilfield, coalmine,
etc.) to extract, process, transport and distribute the fuels used for domestic
and other purposes; it is a quantity that is higher than the calorific value
of those fuels (delivered energy) by an
amount representing the energy cost of extraction, processing, transportation
and distribution of fuels.