
The program 'CASAnova - An Educational Software for Energy and Heating Demand, Solar Heat Gains and Overheating Risk in Buildings' is designed for an easy-to-use handling in order to get an intuitive understanding of the relations between building geometry, orientation, thermal insulation, glazing, solar heat gains, heat energy demand, heating and primary energy as well as overheating in summer.
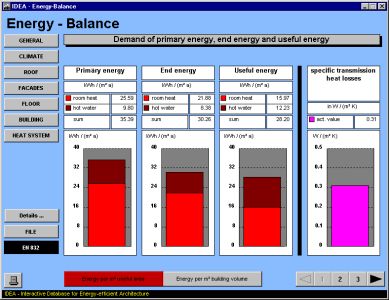
'Energy balance' calculates the required heat energy for heating buildings according to the European Norm EN832.
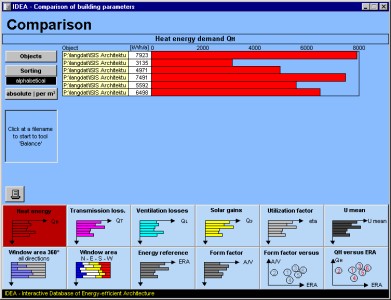
'Comparison' compares buildings which beforehand have been calculated by the Energy balance tool. Items of comparison are, e.g. heat energy demand, transmission and ventilation losses, internal and solar gains, glazing areas, surface-to-volume-ratio etc.
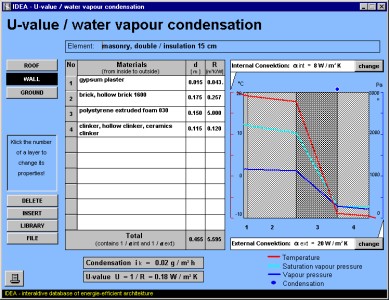
'U-value' determines the transfer of heat and water vapor through a wall which may be composed of different material layers. The user will be informed about the courses of temperature and vapor pressure within the wall construction by a graphical output.
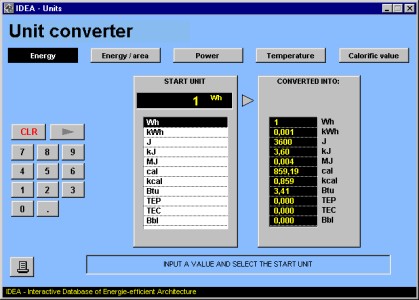
Do you know, how much MJ are 1 kWh or what is the calorific value of 1 m³ natural gas? The tool 'Unit converter' answers such questions and converts equivalent units from one to another.
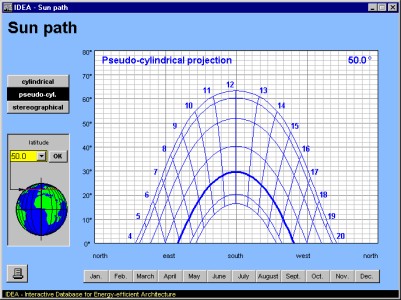
'Sun Path' calculates and visualizes the position of the sun during the course of a day for all days of the year and for all geographical positions.
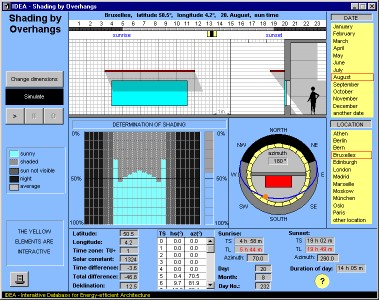
'Shading by overhangs' allows the determination of shadings on south-facing windows due to overhangs. The user can specify the dimensions of window and overhang and observes the course of shading during any given day of the year and for all defined locations.
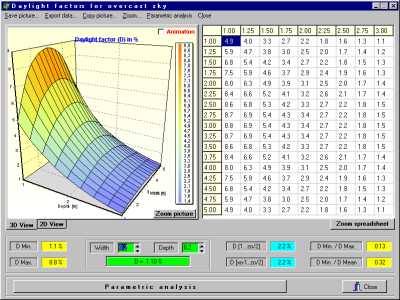
'Daylight' determines daylight factor and illumination intensity at all positions on working plane level for an arbitrary squared room with up to two windows and two horizontal skylights (diffuse sky according to CIE). Moreover a "daylight autonomy factor" can be calculated, which is the percentage of time during which the illumination intensity exceeds a specified limit (e.g. 300 lx).
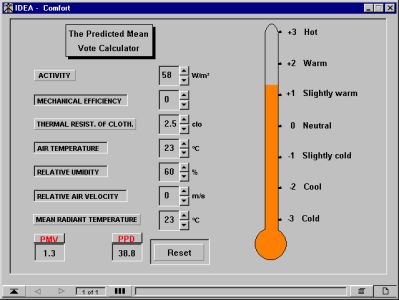
'Thermal comfort' determines the thermal comfort indices predicted mean vote (PMV) and predicted percentage of dissatisfied (PPD) according to the calculation method of P.O. Fanger. By inserting the values of influencing parameters (i.e. indoor air temperature, surface temperatures, air velocity, humidity, activity and clothing) the user will get the corresponding results for PMV and PPD.
Program © Prof. F. Butera, Polytechnicum of Milano, Italia.

'Environmental evaluation' gives a first and coarse assessment concerning the environmental behavior of a building with regard to resources of energy and water.
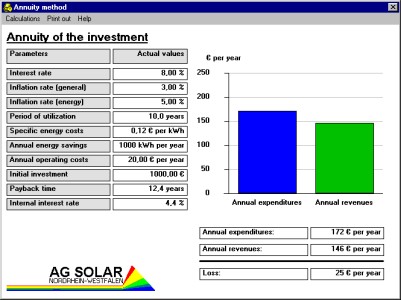
'Economic evaluation' evaluates the economics of measures for energy saving or for the utilization of renewable energies. The tool determines the pay back period (if any), internal interest rate and annuity of any initial investment, for estimated energy savings, energy costs, operating costs, capital interest rate, inflation rate, etc. For cases where no pay back period within the next 100 years will result, several economic conditions are calculated which would make this investment for energy reasonable within the considered period of time.
 further information
further information
 further information
further information

 further information
further information
 further information
further information
 download (5.0 MB)
download (5.0 MB)
 further information
further information
 further information
further information
 further information
further information

 further information
further information
 download (4.4 MB)
download (4.4 MB)

 further information
further information

 further information
further information

 further information
further information
 download (4.1 MB)
download (4.1 MB)

